When it comes to understanding the layout and design of a building, floor plans play a crucial role. Whether you are an architect, a contractor, or simply someone interested in the world of architecture, being able to interpret floor plans is an invaluable skill. In this blog post, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to read a floor plan effectively.
So, let’s dive in!
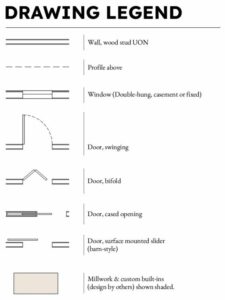
1. Key Components
Walls
Walls are represented by solid lines on the floor plan and define the boundaries of different rooms or spaces.
Doors and Windows
These are usually indicated by openings in the walls. Doors are typically shown as rectangles, while windows are depicted as smaller openings.
Rooms and Spaces
Each room or space is labeled and typically includes dimensions. Pay attention to the size and shape of rooms to understand their intended function.
Furniture and Fixtures
Floor plans may include basic furniture placements to help visualize the layout. These are typically represented by simple shapes like rectangles or circles.
Stairs and Elevators
If the building has multiple floors, staircases and elevators are shown with distinct symbols or annotations.
2. Scale and Measurements
Scale
Pay attention to the scale mentioned on the floor plan. It helps you understand the relationship between the measurements on the plan and the actual dimensions of the building.
Dimensions
Look for dimensions indicated on the floor plan, usually marked in feet or meters. They help you understand the size of the rooms, hallways, and other spaces accurately.
3. Room Labels and Functionality
Room Names
Each room is labeled with a specific name or number, which may indicate its intended use (e.g., bedroom, kitchen, living room).
Room Relationships
Analyze how different rooms are connected to each other. This will help you understand the flow and circulation within the building.
4. Symbols and Abbreviations
Legend
Floor plans often include a legend that explains the symbols and abbreviations used throughout the plan. Refer to it for clarity on the representation of different elements.
Standard Symbols
Some common symbols include electrical outlets, light switches, plumbing fixtures, and ventilation systems. Familiarize yourself with these symbols to understand the building\’s infrastructure.
5. Understanding Spatial Proportions
Proportions and Scale
Analyze the proportions and scale of the rooms in relation to each other. This will give you a sense of the overall size and balance of the building.
Traffic Flow
Study the arrangement of rooms and hallways to determine the flow of movement within the building. This is essential for ensuring functionality and efficiency.
Conclusion
Mastering the skill of reading floor plans is crucial for architects, contractors, and anyone interested in the world of architecture. By understanding the key components, scale and measurements, room labels, symbols, and spatial proportions, you will be able to interpret floor plans accurately and visualize the design concept of a building more effectively. So, the next time you come across a floor plan, remember these tips to unlock the hidden secrets it holds.
Happy reading and exploring the world of architecture!
